 MAXIMA Quick Reference
MAXIMA Quick Reference
Fourier Series Expansion
-
 maxima_totalfourier
maxima_totalfourier
Function: totalfourier (f, x, p) Returns fourexpand (foursimp (fourier (f, x, p)), x, p, 'inf). Function: opsubst (f, g, e) The function opsubst is similar to the function subst, except that opsubst only makes substitutions for the operators in an expression. In general, when f is an operator in the expression e, substitute g for f in the expression e. To determine the operator, opsubst sets inflag to true. This means opsubst substitutes for the internal, not the displayed, operator in the expression. To use this function write first load("opsubst"). Example: (%i) load("fourie")$ (%i) f(x):=x; (%i) totalfourier(f(x),x,1/2); (%o) -('sum((-1)^n*sin(2*%pi*n*x)/n,n,1,inf))/%pi (%i) FF:subst(3,inf,%); (%o) -('sum((-1)^n*sin(2*%pi*n*x)/n,n,1,3))/%pi (%i) load("opsubst")$ (%i) FG:opsubst(sum,'sum,FF); (%o) -sum((-1)^n*sin(2*%pi*n*x)/n,n,1,3)/%pi (%i) define(g(x),FG); (%o) g(x):=-sum((-1)^n*sin(2*%pi*n*x)/n,n,1,3)/%pi
Laplace Tranceform
LAPLACE ... Laplace Tranceform
Function: laplace (expr, t, s)
The Laplace transform of expr with respect to the variable t and transform parameter s.
Example:
Delta Function
(%i) laplace(delta(t), t, s);
(%o) 1
Unit Step Function
(%i) laplace(1, t, s);
(%o) 1/s
Trigonometric Function
(%i) laplace(sin(t), t, s);
(%o) 1/(s^2+1)
(%i) laplace(cos(t), t, s);
(%o) s/(s^2+1)
Exponential Function
(%i) laplace(%e^(-a*t),t,s);
(%o) 1/(s+a)
(%i) laplace(%e^(-a*t)*t^2, t, s);
(%o) 2/(s+a)^3
ILT ... Inverse Laplace Tranceform
Function: ilt (expr, t, s)
The inverse Laplace transform of expr with respect to t and parameter s
Example:
(%i) ilt(1/s^2, s, t);
(%o) t
(%i) ilt(1/s^3, s, t);
(%o) t^2/2
(%i) ilt(1/(s+a), s, t);
(%o) %e^-(a*t)
(%i) ilt(1/(s+a)^2, s, t);
(%o) t*%e^-(a*t)
(%i) ilt((s+a)/((s+a)^2+w^2), s, t);
(%i) ilt(1/((s+2)^2*(s+3)), s, t);
(%i) ilt(1/(s*((s+2)^2+1)), s, t);
Taylor Expansion
-
 maxima_taylor
maxima_taylor
Function: taylor (expr, x, a, n) Function: taylor (expr, [x_1, x_2, ...], a, n) Function: taylor (expr, [x, a, n, 'asymp]) Function: taylor (expr, [x_1, x_2, ...], [a_1, a_2, ...], [n_1, n_2, ...]) Function: taylor (expr, [x_1, a_1, n_1], [x_2, a_2, n_2], ...) Expands of the expression expr in a truncated Taylor or Laurent series in the variable x around the point a, containing terms through (x - a)^n. Example: Trigonometric Expansion (%i) taylor(sin(x), x, 0, 7); (%o) x-x^3/6+x^5/120-x^7/5040 (%i) taylor(cos(x), x, 0, 7); (%o) 1-x^2/2+x^4/24-x^6/720 Exponential Function (%i) taylor(exp(x), x, 0, 7 ); (%o) 1+x+x^2/2+x^3/6+x^4/24+x^5/120+x^6/720+x^7/5040 Summation of Geometric Progression (%i) taylor(1/(1-x), x, 0, 7 ); (%o) 1+x+x^2+x^3+x^4+x^5+x^6+x^7 (%i) taylor(1/(1+x), x, 0, 7 ); (%o) 1-x+x^2-x^3+x^4-x^5+x^6-x^7 (%i) taylor(log(1-x),x,0,7); (%o) -x-x^2/2-x^3/3-x^4/4-x^5/5-x^6/6-x^7/7
Trigonometric
TRIGEXPAND ... Trigonometric Expansion
Function: trigexpand (expr) Expands trigonometric and hyperbolic functions of sums of angles and of multiple angles occurring in expr. Example: Trigonometric expansion (%i) trigexpand(sin(x+y)); (%o) sin(x)*cos(y)+cos(x)*sin(y) (%i) trigexpand(cos(x+y)); (%o) cos(x)*cos(y)-sin(x)*sin(y) (%i) trigexpand(tan(x+y)); (%o) (tan(y)+tan(x))/(1-tan(x)*tan(y)) Double-Angle Formula (%i) trigexpand(sin(2*x)); (%o) 2*cos(x)*sin(x) (%i) trigexpand(cos(2*x)); (%o) cos(x)^2-sin(x)^2 (%i) trigexpand(tan(2*x)); (%o) 2*tan(x)/(1-tan(x)^2)
TRIGREDUCE ... Combines products and powers of trigonometric and hyperbolic
Function:trigreduce(expr, x) Function:trigreduce(expr) Combines products and powers of trigonometric and hyperbolic Example: (%i) trigreduce(sin(x)^2); (%o) (1-cos(2*x))/2 (%i) trigreduce(sin(x)^3); (%o) (3*sin(x)-sin(3*x))/4 (%i) trigreduce(cos(x)^2); (%o) (cos(2*x)+1)/2 (%i) trigreduce(cos(x)^3); (%o) (cos(3*x)+3*cos(x))/4 (%i) trigreduce(-sin(x)^2+3*cos(x)^2+x); (%o) cos(2*x)/2+3*(cos(2*x)/2+1/2)+x-1/2
Matrix
DETERMINANT ... Determinant of a Matrix
Function: determinant (M)
Returns the determinant of the matrix M.
Example:
(%i) determinant( matrix( [1,2], [2,1] ) );
(%o) -3
(%i) determinant( matrix( [a,b], [c,d] ) );
(%o) a*d-b*c
(%i) determinant( matrix( [a,b,c],[d,e,f],[g,h,i] ) );
(%o) a*(e*i-f*h)-b*(d*i-f*g)+c*(d*h-e*g)
 maxima_fourier-transform
maxima_fourier-transform maxima_fourier-transform-plane-square
maxima_fourier-transform-plane-square plot3d
plot3d plot3d-sphere
plot3d-sphere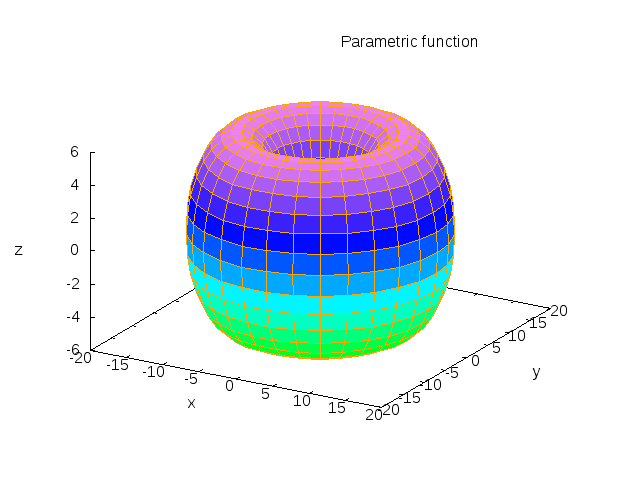 plot3d-torus
plot3d-torus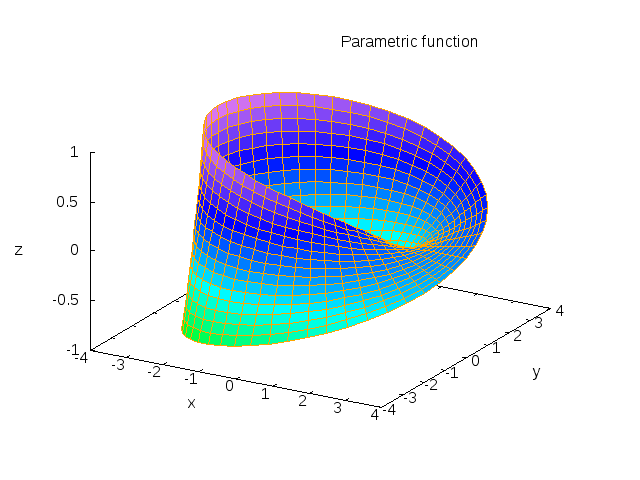 plot3d-Moebius-band
plot3d-Moebius-band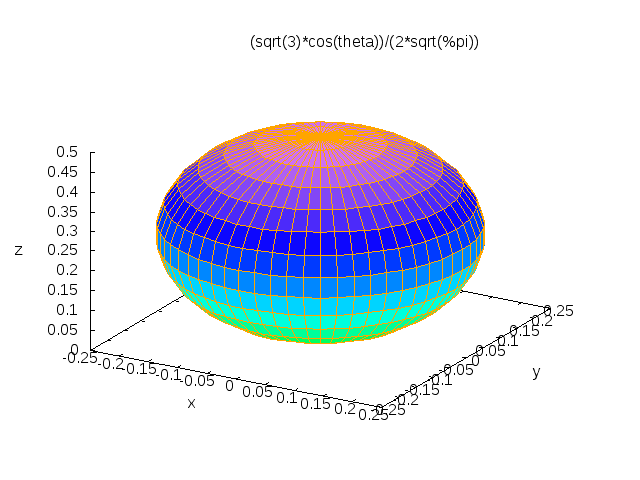 spherical-harmonic
spherical-harmonic Bode Diagram GAIN Plotting
Bode Diagram GAIN Plotting Bode Diagram PHASE Plotting
Bode Diagram PHASE Plotting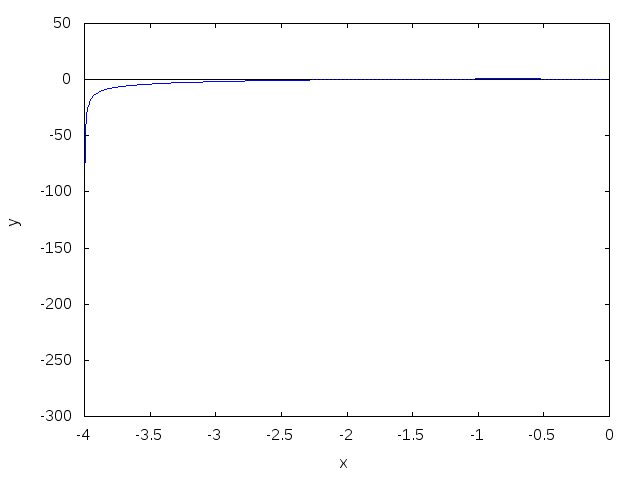 Nyquist Diagram Plotting
Nyquist Diagram Plotting